1 Sites[1]
| CO | Ico | BCC | SC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 10\nu^3/3+5\nu^2+11\nu/3+1 | 10\nu^3/3+5\nu^2+11\nu/3+1 | (2\nu+1)(\nu^2+\nu+1) | (2\nu+1)^3 |
| N_{\sigma} | 10\nu^2+2 | 10\nu^2+2 | 6\nu^2+2 | 24\nu^2+2 |
| D | N_{\sigma}/N | N_{\sigma}/N | N_{\sigma}/N | N_{\sigma}/N |
| N_S | 6(\nu-1)^2 | —- | 6(\nu-1)^2 | 6(2\nu-1)^2 |
| R_S^p | \nu(\nu+2)/8 | —- | \nu(\nu+2)/8 | \nu(\nu+1)/2 |
| R_S^i | (\nu^2-1)/8 | —- | (\nu^2-1)/8 | \nu(\nu+1)/2 |
| N_T | 4(\nu-1)(\nu-2) | 10(\nu-1)(\nu-2) | —- | —- |
| R_T^p | \sum\limits_{\alpha=1}^{m/2}(3\alpha+a)+\sum\limits_{\alpha=1}^{m/2-1}(3\alpha);\nu=3m+a;\alpha=-1,0,1 | \sum\limits_{\alpha=1}^{m/2}(3\alpha+a)+\sum\limits_{\alpha=1}^{m/2-1}(3\alpha);\nu=3m+a;\alpha=-1,0,1 | —- | —- |
| R_T^i | \frac{1+a}{1+|a|}+\sum\limits_{\alpha=1}^{(m-1)/2}(6\alpha+a);\nu=3m+a;\alpha=-1,0,1 | \frac{1+a}{1+|a|}+\sum\limits_{\alpha=1}^{(m-1)/2}(6\alpha+a);\nu=3m+a;\alpha=-1,0,1 | —- | —- |
| N_E | 24(\nu-1) | 30(\nu-1) | 12(\nu-1) | 12(2\nu-1) |
| R_E^p | \nu/2 | \nu/2 | \nu/2 | \nu |
| R_E^i | (\nu-1)/2 | (\nu-1)/2 | (\nu-1)/2 | \nu |
P.S.
- N: Total number of atoms
- N_{\sigma}: Number of atoms in a crust
- N_S: Number of atoms on square faces, S
- R_S^e: Number of shells in which the S-tites are contained (\nu even)
- R_S^o: Number of shells in which the S-sites are contained (\nu odd)
- N_T: Number of atoms on triangular faces, T
- R_T^e: Number of shells in which the T-sites are contained (\nu even)
- R_T^o: Number of shells in which the T-sites are contained (\nu odd)
- N_E: Number of atoms on edges, E
- R_E^e:Number of shells in which the E-sites are contained (\nu even)
- R_E^o:Number of shells in which the &sites are contained (\nu odd)
- D_I: Contribution of the I–sites to the dispersion; {N_I/N;I=S, T, E, V)
- \Nu_C: Number of bonds in the core of a cluster of order \nu;(1/2\times{z}\times{N}(\nu-1))
- \Nu_{SC}: Number of bonds between the surface (\nu) and core (\nu – 1):\sum\limits_I(\uparrow)_IN_I(\nu-1),\sum\limits_I(\downarrow)_IN_I(\nu)
- \Nu_{SS}: Number of bonds on the surface of a cluster of order \nu, \frac{1}{2}\sum\limits_I(\leftrightarrow)_IN_I(\nu)
- \Nu: Number of bonds in a cluster of order \nu, (N_C+N_{SC}+N_{SS})
- \bar{Z}: Cluster average coordination number; 2\Nu(\nu)/N(\nu)
- \bar{Z}_C: Core average coordination number; 2\Nu_C(\nu)/N(\nu-1)
- \bar{Z}_{CS}: Core-surface average coordination number; \Nu_{SC}(\nu)/N_{\sigma}(\nu-1)
- \bar{Z}_{SC}: Surface-core average coordination number; \Nu_{CC}(\nu)/N_{\sigma}(\nu)
- \bar{Z}_{SS}: Surface average coordination number; 2\Nu_{Ss}(\nu)/N_{\sigma}(\nu)
2 Reorganization Energy[2]
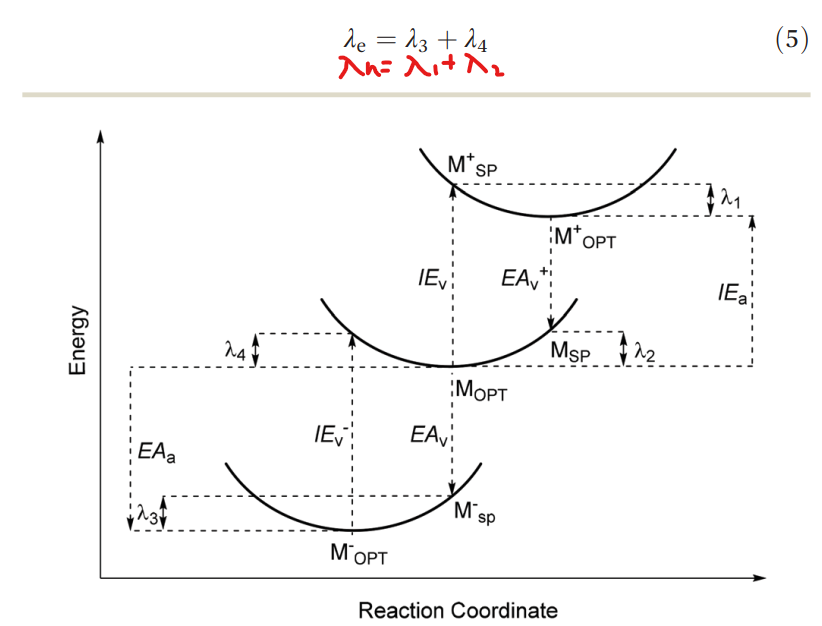 Fig. 1: The ionization energy (IE) and electron affnity (EA) pathways between the anion, neutral and cation potential energy surfaces for the calculation of the hole (electron) reorganization energy \lambda_h (\lambda_e).
Fig. 1: The ionization energy (IE) and electron affnity (EA) pathways between the anion, neutral and cation potential energy surfaces for the calculation of the hole (electron) reorganization energy \lambda_h (\lambda_e).
Ref.
[1]
Montejano-Carrizales, J. M.; Aguilera-Granja, F.; Morán-López, J. L. DIRECT ENUMERATION OF THE GEOMETRICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CLUSTERS. Nanostruct. Mater. 1997, 8, 269–287.
[2]
Jones, L.; Lin, L.; Chamberlain, T. W. Oxygen, Sulfur and Selenium Terminated Single-Walled Heterocyclic Carbon Nanobelts (SWHNBs) as Potential 3d Organic Semiconductors. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 7639–7648.